To get a better vision into the future of “Cloud Computing” for small and medium-sized businesses (SMB’s), it is interesting to look back at the beginning and the creation of Cloud Computing first.
– 1950s: Mainframe and time-sharing
– 1970s: Client-server
– 1990s: Use of cloud in IT structure
– 1999: Launch of Salesforce and Google
– 2000: Multi-user access and plugins
– 2004: Facebook
– 2005: Virtualization and hosting
– 2006: Amazon web services
– 2008: Dropbox
– 2009: Google Apps
– 2011: Hybrid Clouds – iCloud
– 2012: Google Drive
It started in the 1950s, when the first computer mainframe appeared and was made available for corporations and in academia. Also since space and resources didn’t allow it, people were introduced to time-sharing for the first time.This brought the concept of shared and centralized compute resources. The “second generation” transistor-based computers are replacing vacuum-tube machines by late 1950. The IBM 1401 came out, which gave smaller businesses access to data processing computers. The 1401 was so popular that mid-60s, almost half of the world’s computer systems were 1401 with 12,000 units sold in total.
Late 1970s, the term “client-server” comes into use, defining the compute model where clients access data and applications from a central server over a local area network.
In mid 1990s, businesses started using the word cloud in their IT structure.
1999 marks the industry shift to Cloud Computing and to Social Enterprise. Salesforce is created and becomes the first company to make business applications available from an internet website. Google is launched as well, and provides a remarkable search service that brings impressive results. By that time ten thousand search queries were made daily.
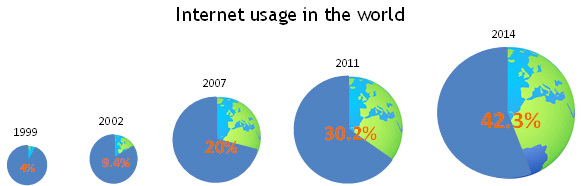
In January 1999 about 4% of the world’s population uses the internet and by September 3.5 million search queries were answered daily by Google.
On the verge of the new century, working habits changed for SMB’s. They now needed multiple users to work on the same application and the same file concurrently. Some software companies started creating extensions, adds-on and plugins to allow the application to communicate with other systems.
In 2004, Facebook is created, allowing people to share personal information with other users.
A year later, with the expansion of networks and people being mobile, virtualization and hosting began. Virtualization and hosting enable companies to separate the hardware from the operating system and offer multiple virtual desktop on the same computer: meaning the application can be accessed by multiple users at the same time.
In December 2005, about 15.7% of the world’s population uses the internet.
Then in 2006 Amazon launches “Amazon Web Services”, a collection of remote computing services that provides online services for other web sites or client-side applications.
In December 2007 the worldwide internet usage jumps to 20% and 1.2 billion search queries were answered by Google on a daily average.
In 2008, Dropbox was launched. It’s the first file hosting service that offers cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud and client software.
Browser-based cloud enterprise applications like Google Apps are introduced in 2009. This revolutionizes the market for productivity applications and free users from their desktops.
Hybrid Cloud emerges in 2011, combining public and private cloud. Later this year, Apple launches iCloud, a wireless file hosting service for Apple products. By March 2011, 30.2% of the world’s population uses the internet.
2012, Google launches Google Drive a free cloud storage for digital files.
By June 2014, 42.3% of the world’s population uses the internet and Google answers 5.74 billion search queries on a daily average.
With Cloud Computing and the rise of smartphone usage, the personal computer space is now mobile and accessible anywhere. This growth for working outside the office will raise some challenges and opportunities.
Here is what to expect in the following years with the fast growing spread of Cloud Computing:
1) Fewer people will be sitting in their office, as technology will enable them to stay home. This will on the other hand help businesses reduce office costs.
2) Work mobility and cloud technology means workers can still have access at anytime. The downside of this development is that there will be longer hours that are unmanaged.
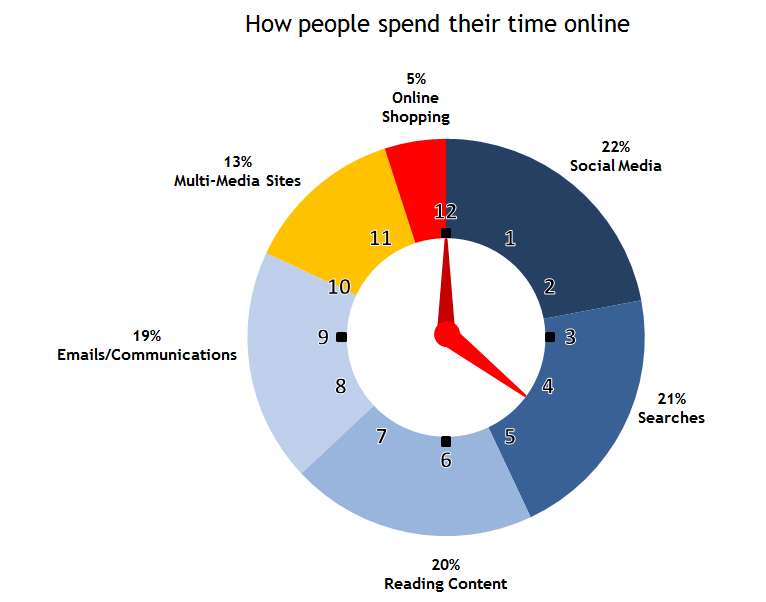
3) Fewer face-to-face meetings. People prefer using business communication tools such as email, text messaging and web meetings rather than in-person conferences.
4) More emails. People using Internet for their work say that emailing is a key factor for communication. Some companies eliminated voicemail in favor of email.
_______________________________________________________________________
About MyQuickCloud
MyQuickCloud – Remote Access Rebooted
We believe that elaborate software should not only be reserved for large companies, that’s why we created MyQuickCloud, the cloud enabler for any desktop application. With our technology you can work and collaborate from anywhere at anytime, by instantly turning any of your favorite desktop programs into online apps, with or without hosting.
To discover more please visit myquickcloud.com