In terms of data storage and software, cloud computing is the future. When businesses move to the cloud, they can experience significant benefits, including increased convenience and reduced costs. This article explains exactly what the cloud is, how it can benefit your business, and whether or not it is worthwhile to invest in it.
You can use cloud computing to store data, share information, and use software by using the internet instead of your computer.
Applications are hosted on secure servers and accessed over the internet – or ‘in the cloud’ – rather than being purchased and installed on your computer.
A secure internet connection is required to access the cloud. Web browsers (such as Chrome or Internet Explorer) and apps you download to your computer, or mobile devices, allow you to access some software and storage.
Storage and processing are done virtually, so there’s no need for a network server – but the advantages don’t stop there.
The possibilities at Microsoft UK are still expanding, according to Robert Epstein, head of small business sales and marketing.
“What is new is the huge and growing variety of software, and the fact that cloud is now much more effective because of greater bandwidth and faster connections.”
Most businesses pay a monthly fee to a cloud provider, such as Google or Microsoft. Rather than owning the software, you license it, paying a regular subscription fee.
Email, CRM software, accounting software, and databases are among the cloud applications used by small businesses.
In addition to productivity software, you can also store data online with cloud systems. Rather than saving documents and data to a hard drive or network server, you can save them to the cloud.
Services vary in cost, but they are affordable. Small business packages from Microsoft cost about £9-£11 per user per month and include email, data sharing and web conferencing.
Flexible IT solutions
“Cloud computing can offer small businesses a lot of flexibility,” says Epstein. “It’s accessible anywhere, anytime from any device that connects to the internet.”
As well as being good value for money, it is also good for the environment. As opposed to purchasing standalone software for each computer or network, you pay a monthly fee. Cloud computing makes productivity software more affordable than ever, but you’ll need a license for each user.
When you store data in the cloud, you can access it anywhere, anytime, and on (almost) any device connected to the internet. Using your mobile phone, you can check and edit Word documents, then log in to your laptop to finish them.
The cloud software keeps you free of the time-consuming, and often confusing, task of updating it. You’ll always be using the most up-to-date version because the software provider performs all updates, upgrades, and maintenance behind the scenes.
“This can help you operate on a more level playing field with big companies, because you can access the latest, sophisticated software without high levels of investment,” explains Epstein.
Cloud services
Cloud computing services include productivity software, data storage, design packages, and more. The following are some of the most popular among small businesses:
- Dropbox – helps you backup and share files with others.
- Microsoft 365 – access files anywhere online or offline and across devices with Microsoft’s Business Standard package.
- QuickBooks – cloud accounting software from Intuit.
- Salesforce – customer relationship management (CRM).
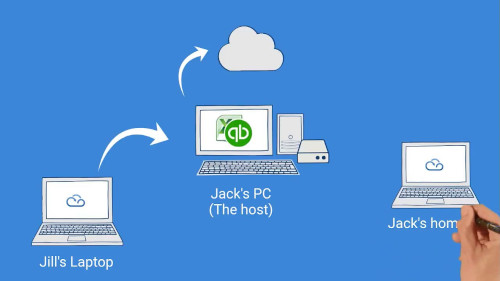
- MyQuickCloud –
Drawbacks of cloud computing
To use cloud solutions, you’ll need a stable internet connection, which may not be suitable for all users. You may not be able to access critical data if your internet connection is down, for example.
Choosing a cloud software provider you can trust is essential. You’ll find all the big names in software offering cloud solutions. To learn from others’ experiences, check online reviews.
Cloud-based businesses should check service level agreements carefully before signing, say experts. Ensure they can handle your business needs and always ask about their security standards, advises Epstein.
“It’s pointless to change your IT setup just for the sake of changing it,” he concludes. “However, if your email package is slow or you’re thinking of upgrading, it’s worth considering.”
Cloud-based preparations
Your business will undergo a fundamental change when you adopt cloud technology. Additionally, it will transform how your company purchases and provides IT services. Consult the experts before taking the plunge to evaluate the costs and benefits.
Before adopting cloud computing, consider these seven key factors:
- Establish your goals and why you want them. Understand what improvements you want the cloud to bring. Evaluate cloud services alongside other options and weigh their advantages and disadvantages.
- Make sure you understand your overall business needs, not just your IT needs. Businesses use cloud computing to make their systems more efficient. Cloud computing, however, can mean fundamental changes to your IT infrastructure as well as ending familiar services and procedures, so it’s vital the proposed changes are well suited to your whole business. This kind of change might not be justified solely on the basis of cost savings.
- Make sure you prepare thoroughly. Introducing cloud computing should be planned meticulously. Develop a plan for its adoption, management, and monitoring. With ‘on demand’ cloud services, you can try out different options before rolling them out across your organization.
- Reduce the complexity and the cost. A small monthly fee makes cloud services appear cheap. If you add bolt-ons or additional user accounts, those monthly fees can add up quickly. Also, keep in mind that things can get more complicated. It will be up to you to figure out how to manage your cloud supplier(s) and how to integrate the different parts of your business IT.
- Consider the risks. Is your data safe and secure? Is the cloud computing provider you have chosen reliable and experienced? The security of your data is a serious concern, so choose a service that employs robust cyber security measures and is GDPR compliant.
- It is important to choose the right partner. Cost alone shouldn’t be the deciding factor. The same care should be taken when selecting your suppliers as you would with any other key provider. It is important to know how and where your data is stored and protected, what level of service is guaranteed, what support is available, and when.
- Establish a service level agreement (SLA). You need cloud computing to be reliable if you plan on using it. SLAs guarantee availability and how fast you’ll receive a response if there’s a problem.
After considering the points above, you should be able to assess how cloud computing can benefit your business. A roadmap of how you can implement cloud software will also enable you to minimize disruptions, eliminate risks, and maximize returns.
A beginner’s guide to cloud computing
In terms of data storage and software, cloud computing is the future. When businesses move to the cloud, they can experience significant benefits, including increased convenience and reduced costs. This article explains exactly what the cloud is, how it can benefit your business, and whether or not it is worthwhile to invest in it.
You can use cloud computing to store data, share information, and use software by using the internet instead of your computer.
Applications are hosted on secure servers and accessed over the internet – or ‘in the cloud’ – rather than being purchased and installed on your computer.
A secure internet connection is required to access the cloud. Web browsers (such as Chrome or Internet Explorer) and apps you download to your computer, or mobile devices, allow you to access some software and storage.
Storage and processing are done virtually, so there’s no need for a network server – but the advantages don’t stop there.
The possibilities at Microsoft UK are still expanding, according to Robert Epstein, head of small business sales and marketing.
“What is new is the huge and growing variety of software, and the fact that cloud is now much more effective because of greater bandwidth and faster connections.”
Most businesses pay a monthly fee to a cloud provider, such as Google or Microsoft. Rather than owning the software, you license it, paying a regular subscription fee.
Email, CRM software, accounting software, and databases are among the cloud applications used by small businesses.
In addition to productivity software, you can also store data online with cloud systems. Rather than saving documents and data to a hard drive or network server, you can save them to the cloud.
Services vary in cost, but they are affordable. Small business packages from Microsoft cost about £9-£11 per user per month and include email, data sharing and web conferencing.
Flexible IT solutions
“Cloud computing can offer small businesses a lot of flexibility,” says Epstein. “It’s accessible anywhere, anytime from any device that connects to the internet.”
As well as being good value for money, it is also good for the environment. As opposed to purchasing standalone software for each computer or network, you pay a monthly fee. Cloud computing makes productivity software more affordable than ever, but you’ll need a license for each user.
When you store data in the cloud, you can access it anywhere, anytime, and on (almost) any device connected to the internet. Using your mobile phone, you can check and edit Word documents, then log in to your laptop to finish them.
The cloud software keeps you free of the time-consuming, and often confusing, task of updating it. You’ll always be using the most up-to-date version because the software provider performs all updates, upgrades, and maintenance behind the scenes.
“This can help you operate on a more level playing field with big companies, because you can access the latest, sophisticated software without high levels of investment,” explains Epstein.
Cloud services
Cloud computing services include productivity software, data storage, design packages, and more. The following are some of the most popular among small businesses:
- Dropbox – helps you backup and share files with others.
- Microsoft 365 – access files anywhere online or offline and across devices with Microsoft’s Business Standard package.
- QuickBooks – cloud accounting software from Intuit.
- Salesforce – customer relationship management (CRM).
- MyQuickCloud – MyQuickCloud is a secure cloud office. Each user has its own dedicated desktop workspace to open from anywhere. Users connect to the same desktop while in the office or outside.
Drawbacks of cloud computing
To use cloud solutions, you’ll need a stable internet connection, which may not be suitable for all users. You may not be able to access critical data if your internet connection is down, for example.
Choosing a cloud software provider you can trust is essential. You’ll find all the big names in software offering cloud solutions. To learn from others’ experiences, check online reviews.
Cloud-based businesses should check service level agreements carefully before signing, say experts. Ensure they can handle your business needs and always ask about their security standards, advises Epstein.
“It’s pointless to change your IT setup just for the sake of changing it,” he concludes. “However, if your email package is slow or you’re thinking of upgrading, it’s worth considering.”
Cloud-based preparations
Your business will undergo a fundamental change when you adopt cloud technology. Additionally, it will transform how your company purchases and provides IT services. Consult the experts before taking the plunge to evaluate the costs and benefits.
Before adopting cloud computing, consider these seven key factors:
- Establish your goals and why you want them. Understand what improvements you want the cloud to bring. Evaluate cloud services alongside other options and weigh their advantages and disadvantages.
- Make sure you understand your overall business needs, not just your IT needs. Businesses use cloud computing to make their systems more efficient. Cloud computing, however, can mean fundamental changes to your IT infrastructure as well as ending familiar services and procedures, so it’s vital the proposed changes are well suited to your whole business. This kind of change might not be justified solely on the basis of cost savings.
- Make sure you prepare thoroughly. Introducing cloud computing should be planned meticulously. Develop a plan for its adoption, management, and monitoring. With ‘on demand’ cloud services, you can try out different options before rolling them out across your organization.
- Reduce the complexity and the cost. A small monthly fee makes cloud services appear cheap. If you add bolt-ons or additional user accounts, those monthly fees can add up quickly. Also, keep in mind that things can get more complicated. It will be up to you to figure out how to manage your cloud supplier(s) and how to integrate the different parts of your business IT.
- Consider the risks. Is your data safe and secure? Is the cloud computing provider you have chosen reliable and experienced? The security of your data is a serious concern, so choose a service that employs robust cyber security measures and is GDPR compliant.
- It is important to choose the right partner. Cost alone shouldn’t be the deciding factor. The same care should be taken when selecting your suppliers as you would with any other key provider. It is important to know how and where your data is stored and protected, what level of service is guaranteed, what support is available, and when.
- Establish a service level agreement (SLA). You need cloud computing to be reliable if you plan on using it. SLAs guarantee availability and how fast you’ll receive a response if there’s a problem.
After considering the points above, you should be able to assess how cloud computing can benefit your business. A roadmap of how you can implement cloud software will also enable you to minimize disruptions, eliminate risks, and maximize returns.